The Batoms object
The Batoms object is a collection of atoms plus Bcell object and other derivative properties (bonds and so on). Here is how to define a H2O molecule:
from batoms import Batoms
h2o = Batoms("h2o",
species = ["O", "H", "H"],
positions= [[0, 0, 0], [0, -0.76, -0.6], [0, 0.76, -0.6]])
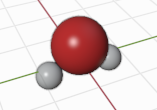
Here, the argument specifies the type of the atoms and their positions. Other
possible keywords are: pbc, cell, atoms, model_style, color_style, radius_style, polyhedra_style, boundary, wrap, and draw.
One get and set model_style, pbc, wrap, cell and boundary by:
>>> h2o.model_style = 0
>>> h2o.pbc = True
>>> h2o.cell = [[3, 0, 0], [0, 3, 0], [0, 0, 3]]
>>> h2o.wrap = False
Here is how you could define an gold crystal structure with a lattice constant of 4.08 Å:
from batoms import Batoms
a = 4.08
positions = [[0, 0, 0], [a/2, a/2, 0], [a/2, 0, a/2], [0, a/2, a/2]]
au = Batoms(label = "au",
species = ["Au"]*len(positions),
positions = positions,
pbc = True,
cell = (a, a, a))

We can also use an Atoms object from ASE.
>>> from ase.build import molecule
>>> from batoms import Batoms
>>> atoms = molecule('H2O')
>>> h2o = Batoms(label = 'h2o', from_ase = atoms)

Here, the keyword from_ase specifies the ase Atoms object.
We can also read an structure from a file:
>>> from batoms.bio import read
>>> tio2 = read('docs/source/_static/datas/tio2.cif')
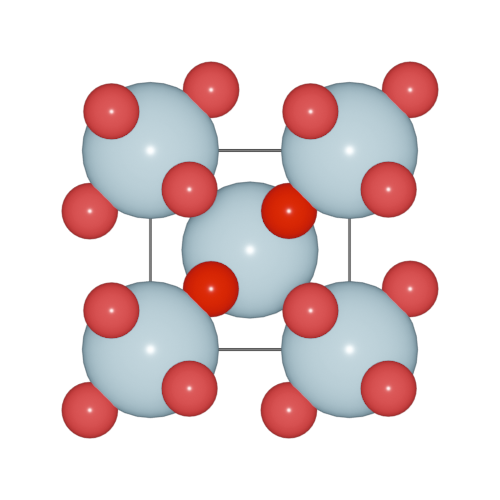
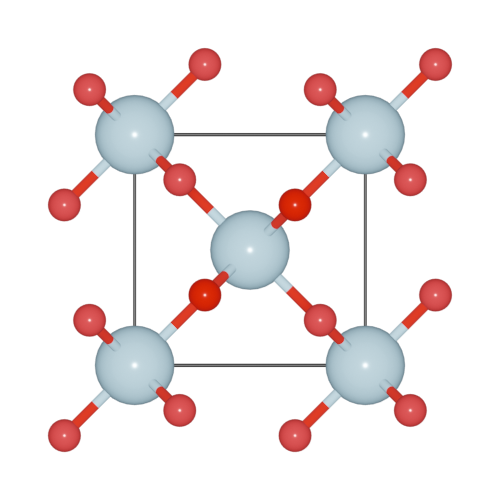
Model_style
One set the model_style by:
>>> h2o.model_style = 1
Here, four models are supported.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
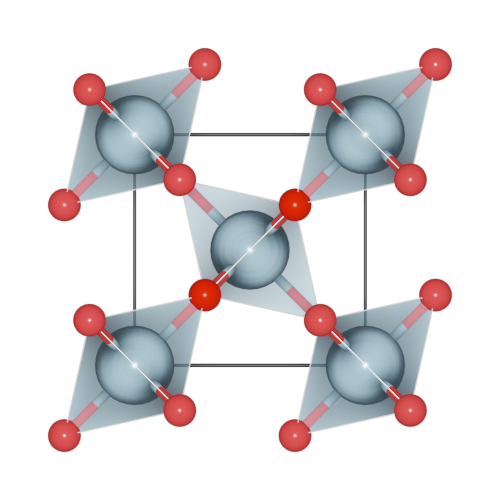
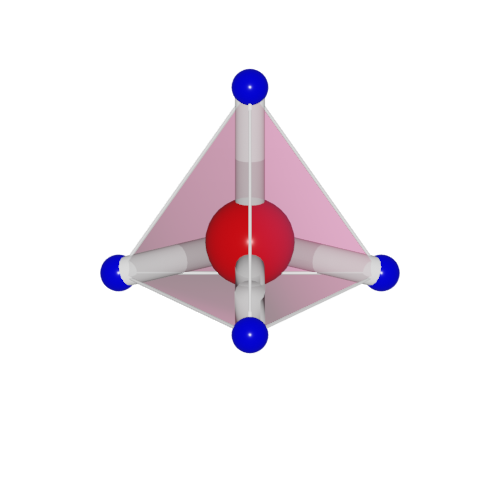
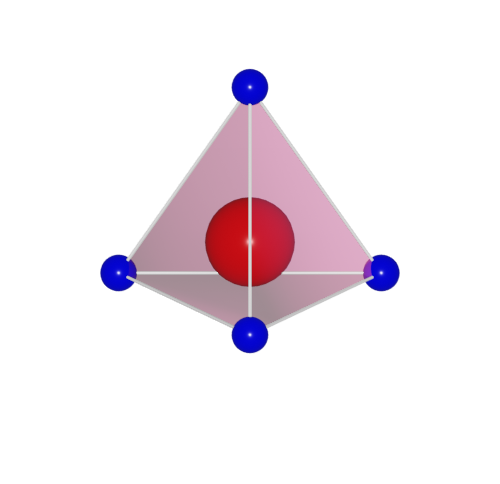
Polyhedra_style
One set the polyhedra_style by:
>>> h2o.polyhedra_style = 1
Here, four polyhedra model are supported.
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
Individual Atom
One get and set the properties of individual atom by (Here is the first atom):
>>> h2o[0].position
>>> h2o[0].scale = 1.2
Other methods
translate()
For example, move h2o molecule by a vector [0, 0, 5],
>>> h2o.translate([0, 0, 5])
rotate()
For example, rotate h2o molecule 90 degree around ‘Z’ axis:
>>> h2o.rotate(90, 'Z')
copy()
For example, copy h2o molecule:
>>> h2o_new = h2o.copy(label = 'h2o_new')
delete()
For example, delete the second atom in h2o molecule. Please note that index start from 0.
>>> h2o.delete([1])
replace()
For example, replace the all H in h2o molecule by S.
>>> h2o.replace([1], 'S')
repeat()
>>> from ase.build import bulk
>>> from batoms import Batoms
>>> au = bulk('Au', cubic = True)
>>> au = Batoms(from_ase = au)
>>> au.repeat([2, 2, 2])
extend()
>>> from ase.build import molecule, fcc111
>>> from batoms import Batoms
>>> import numpy as np
>>> co = molecule('CO')
>>> co = Batoms(label = 'co', from_ase = co)
>>> au = fcc111('Au', (5, 5, 4), vacuum=5.0)
>>> au = Batoms(label = 'au', from_ase = au)
>>> co.translate(au[-1].position + np.array([0, 0, 2.5]))
>>> au.extend(co)
or,
>>> au = au + co
set_boundary()
Set boundary
>>> from batoms import Batoms
>>> from ase.io import read
>>> atoms = read('docs/source/_static/datas/tio2.cif')
>>> tio2 = Batoms(label = 'tio2', from_ase = atoms)
>>> tio2.boundary = 0.5
write()
Save atoms to file, please vist write method in ASE, https://wiki.fysik.dtu.dk/ase/ase/io/io.html?highlight=write#ase.io.write
>>> au.write('au111-co.cif')
get_distances()
>>> h2o.get_distances(0, [1, 2])
get_angle()
>>> h2o.get_angle(0, 1, 2)
Show the species symbol of atoms.
>>> au.show_label = 'species'
get_image()
Render the atoms, and save to a png image.
>>> h2o.get_image(viewport = [1, 0, 0], output_image = 'h2o.png')