The MolecularSurface object
The MolecularSurface object is used to draw molecular surface for Batoms. It has a settings attribute (MolecularSurfaceSettings object), which stores and sets all parameters related to molecular surface. Here the molecular surface includes:
Solvent accessible surface (SAS)
van der Waals surface, a special case of SAS with probe radius equal to 0)
Solvent-excluded surface (SES) or Connolly surface
Model
There are many methods and publications for the visualization of molecular surfaces. In Batoms, two methods are used.
Meshgrid
Find minimum box
Build meshgrid
Calculate power distance for grids
Use marching cube to find isosurface
Metaball
Density from given metaball at given position is calculated by this equation in Blender:
Where
r = distance from center
R = metaball radius
s - metaball stiffness
Density at given position form all metaballs is given by:
The isosurface then build by the BVH algorithm.
Solvent accessible surface
Here we show an example of drawing SAS for the protein kras.
>>> from ase.io import read
>>> from batoms import Batoms
>>> kras = read("kras.pdb")
>>> kras = Batoms("kras", from_ase = kras)
>>> kras.molecular_surface.draw()
>>> kras.get_image(padding = 3, output = "ms_sas_kras.png")
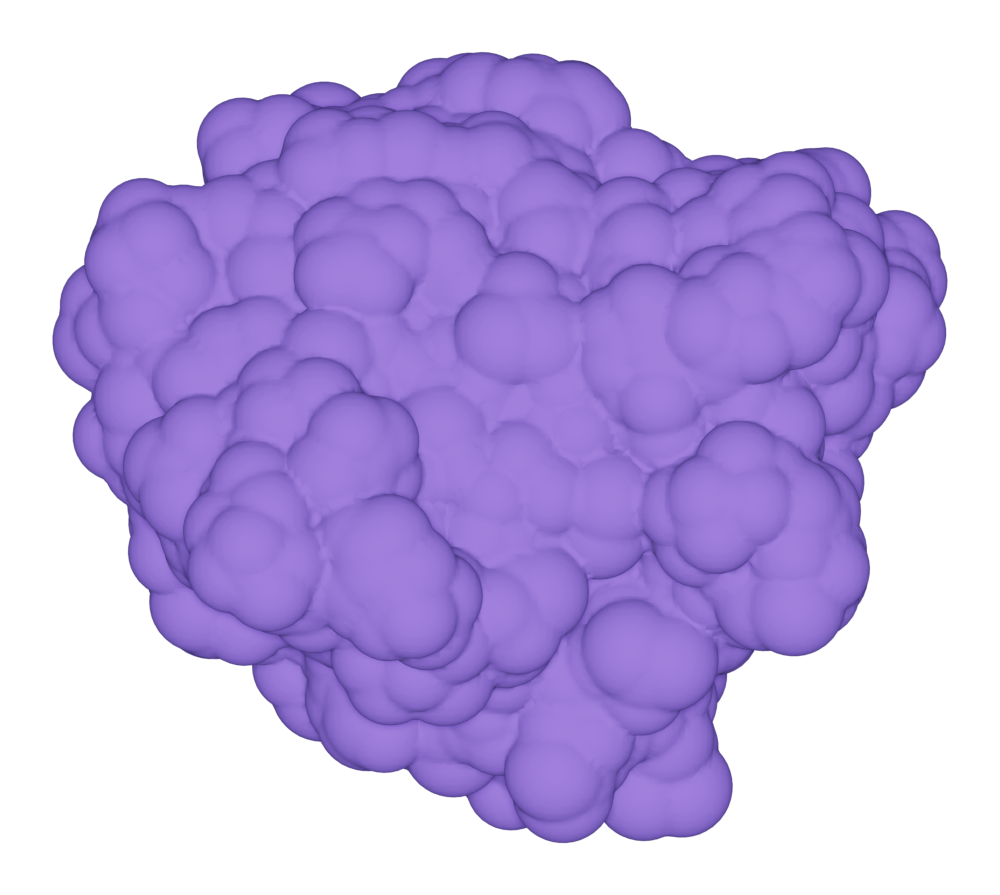
You can get the solvent accessible surface area (SASA) by:
>>> area = kras.molecular_surface.get_sasa()[0]
Solvent-excluded surface
Here we show an example of drawing SES for the protein kras.
>>> from ase.io import read
>>> from batoms import Batoms
>>> kras = read("kras.pdb")
>>> kras = Batoms("kras", from_ase = kras)
>>> kras.molecular_surface.settings["1"].type = "SES"
>>> kras.molecular_surface.draw()
>>> kras.get_image(padding = 3, output = "ms_ses_kras.png")
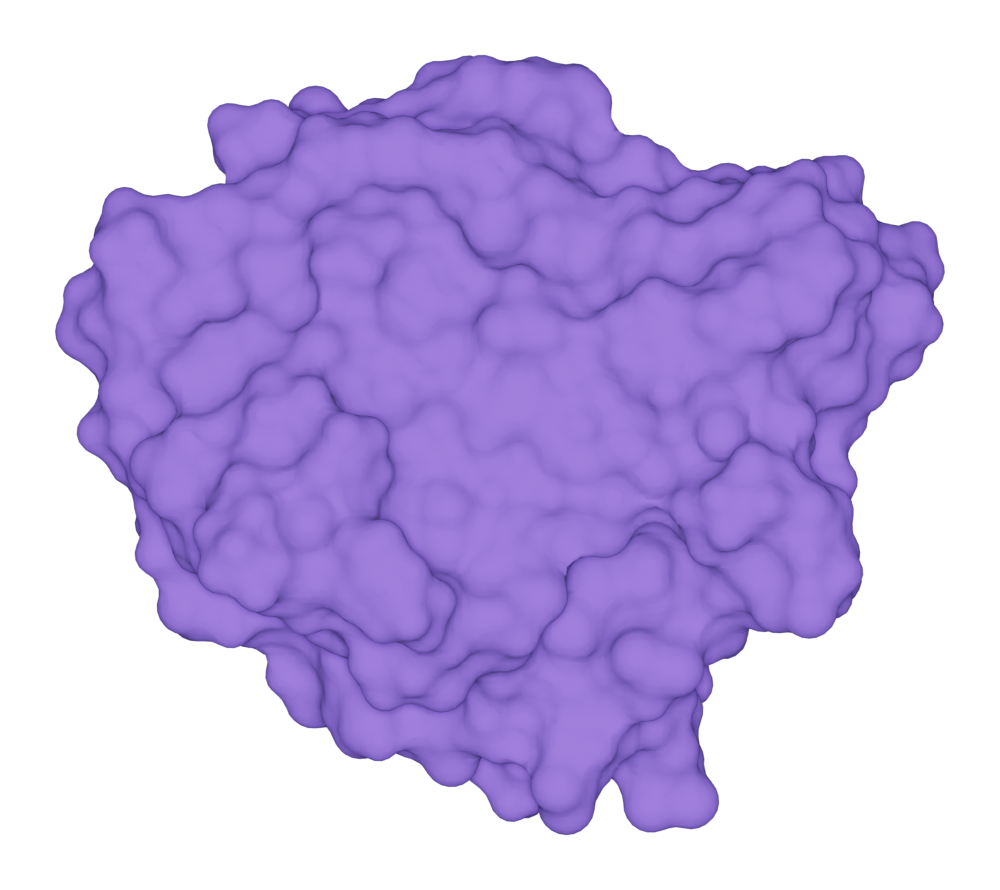
You can get the solvent-excluded surface area (SESA) by:
>>> area = kras.molecular_surface.get_sesa()