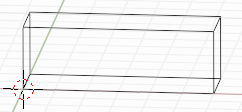
The Bcell object
The Bcell object is an object for unit cell. Here is how to creat a cubic unit cell:
>>> from batoms.cell import Bcell
>>> pt = Batoms(label = 'pt')
>>> pt.cell = [3.98, 3.98, 3.98]
Here, the label keyword to specify the name, and array keyword to specify the size. Other possible keyword are: location.
See the cell:
>>> pt.cell
Cell([[3.98, 0.0, 0.0], [0.0, 3.98, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 3.98]])
>>> pt.cell.length
array([3.98000002, 3.98000002, 3.98000002])
>>> pt.cell.reciprocal
array([[1.57868977, 0. , 0. ],
[0. , 1.57868977, 0. ],
[0. , 0. , 1.57868977]]
Set the cell component:
>>> pt.cell[2, 2] += 5
More details
A cell contains four vertices and 12 edges, and is a three-dimensional object. However, only the first four vertices are independent. Therefore, editing these four vertices will change the positoins of the edges.
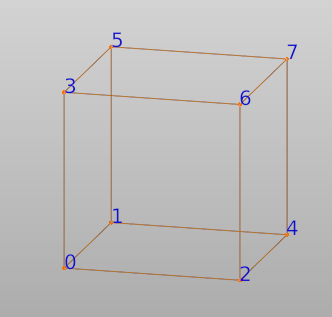
The cell vectors are caculated by:
a = vertices[1] - vertices[0]
b = vertices[2] - vertices[0]
c = vertices[3] - vertices[0]
In this case, the origin is translated to vertices[0]. While the orientation is reserved.
Other methods
copy()
For example, copy cell:
>>> cell_new = pt.cell.copy('pt_new')
repeat()
>>> pt.cell.repeat([3, 1, 1])